
Hi, help us enhance your experience
Hi, help us enhance your experience
Hi, help us enhance your experience
1278 Views
Team eMediNexus 26 September 2024
Introduction1, 2, 3
• Asthma is caused by inflammation and tightening of the muscles around the airways, making it difficult to breathe.
• Symptoms include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. These can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
• Avoiding triggers can help reduce asthma symptoms.
• Most asthma-related deaths occur in low- and lower-middle-income countries due to under-diagnosis and under-treatment.
• Poor control of asthma symptoms increases the risk of exacerbations.
• Inhaled medications can manage asthma symptoms and help people live normal, active lives.

Challenges in Asthma Management 4, 5
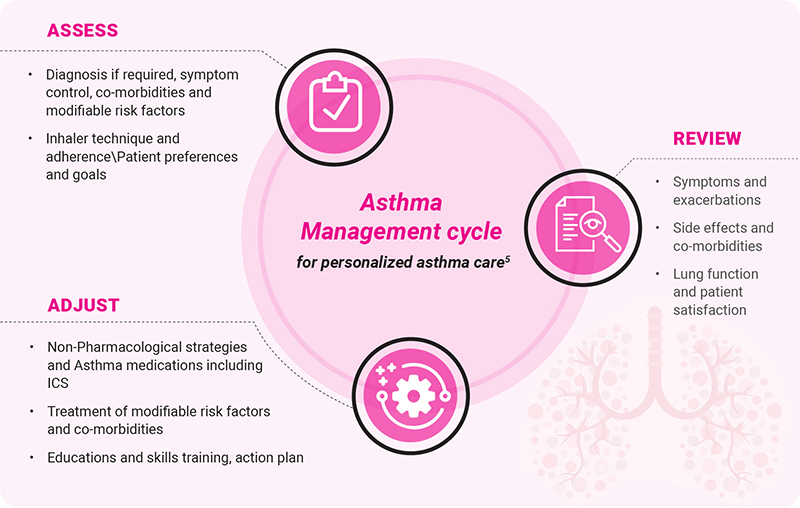
Treatment modalities 5,6,7,8
· Asthma control or management involves two distinct domains: symptom control and risk reduction.
· The treatment of asthma typically follows a stepwise approach employing two categories of medication: relievers and controllers.
o Reliever medications, such as short-acting beta2-agonists (SABA), swiftly alleviate acute symptoms when they arise
Research shows that some patients only use asthma treatment when symptoms occur, avoiding it if they don't feel it's necessary. During exacerbations, these patients often resort to reliever therapies, potentially leading to excessive use of SABAs and underuse of ICS.
Overuse: 7, 8
Overuse of short-acting β2-agonists (SABA) may indicate:
· Poor asthma control
· Adverse health outcomes and
·
Associated with increased risks
of exacerbation and mortality.
Evidences:7
A study by Nwaru et al. (2020) showed that many asthma patients in Sweden were overusing short-acting beta-agonists (SABA). This overuse was linked to a higher risk of asthma flare-ups and increased chances of death from all causes, including respiratory issues and asthma. These results highlight the importance of carefully monitoring SABA usage to improve asthma management.
The Synergy of ICS and SABA 9, 10
· Many studies have shown that combination therapy provides complementary and synergistic effects in treating asthma
· Using inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) with short-acting beta-agonists (SABA) offers significant benefits in asthma management
· ICS helps control inflammation and reduces the frequency of asthma attacks, leading to long-term stability
· SABA provides quick relief from acute symptoms by relaxing the airway muscles.
· When combined, ICS and SABA offer immediate symptom control while targeting underlying inflammation, leading to better overall asthma control, fewer exacerbations, and improved quality of life.
- Using ICS and SABA together in a single inhaler device enhances asthma management by maximizing their complementary effects.
- Combination therapy with ICS-SABA as an anti-inflammatory reliever reduces the risk of severe asthma flare-ups compared to using SABA alone.
Evidences: 6, 11
Conclusion
References:
1. Asthma: WHO; 2024 [cited 2024 30-Aug-24]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma#:~:text=Asthma%20is%20a%20chronic%20lung%20disease%20affecting%20people,severe%20and%20can%20come%20and%20go%20over%20time.
2. InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. Asthma: Learn More – Medication for people with asthma. [Updated 2022 Jul 15]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279519/
3. POCKET GUIDE FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION: GINA; 2023 [cited 2024 1-Apr-24]. Available from: GINA Pocket Guide 2023 (ginasthma.org)…
4. Ioniuc I, Miron I. Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma. 2022;15(12).
5. Global stratergy for Asthma Management and prevention: GINA; 2024 [cited 2024 30-Aug-24]. Available from: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/GINA-2024-Strategy-Report-24_05_22_WMS.pdf.
6. Papi A, Blasi F, Canonica GW, Morandi L, Richeldi L, Rossi A. Treatment strategies for asthma: reshaping the concept of asthma management. Allergy, asthma, and clinical immunology : official journal of the Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2020;16:75.
7. Nwaru BI, Ekström M, Hasvold P, Wiklund F, Telg G, Janson C. Overuse of short-acting β(2)-agonists in asthma is associated with increased risk of exacerbation and mortality: a nationwide cohort study of the global SABINA programme. 2020; 55(4).
8. Medication for people with asthma Cologne, Germany: NIH; Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. 2008 [updated Nov 2021; cited 2024 1-Mar-24]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279519/.
9. Saleh JA. Combination therapy in asthma: a review. Nigerian journal of medicine : journal of the National Association of Resident Doctors of Nigeria. 2008;17(3):238-43
10. Baggott C, Beasley R. Asthma in the anti-inflammatory reliever therapy era. The Lancet Respiratory medicine. 2020.
{{Article_Title}}
{{Article_Author}}
{{Article_Title}}
{{Article_Author}}